Page 120 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 120
Activity ______________ 9.6
• Take a beaker filled with water.
• Take a piece of cork and an iron nail of
equal mass.
• Place them on the surface of water.
• Observe what happens.
The cork floats while the nail sinks. This
happens because of the difference in their
densities. The density of a substance is
defined as the mass per unit volume. The
(a)
density of cork is less than the density of
water. This means that the upthrust of water
on the cork is greater than the weight of the
cork. So it floats (Fig. 9.5).
(b)
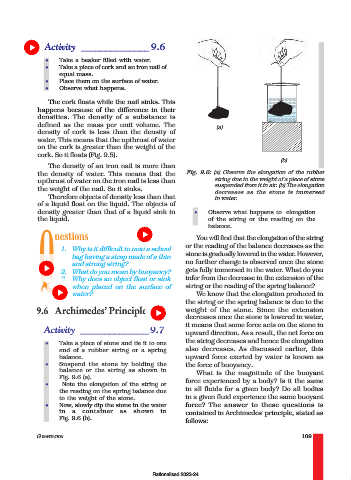
The density of an iron nail is more than
the density of water. This means that the Fig. 9.6: (a) Observe the elongation of the rubber
string due to the weight of a piece of stone
upthrust of water on the iron nail is less than
suspended from it in air. (b) The elongation
the weight of the nail. So it sinks.
decreases as the stone is immersed
Therefore objects of density less than that in water.
of a liquid float on the liquid. The objects of
density greater than that of a liquid sink in • Observe what happens to elongation
the liquid. of the string or the reading on the
balance.
Q 1. Why is it difficult to hold a school or the reading of the balance decreases as the
uestions
You will find that the elongation of the string
stone is gradually lowered in the water. However,
bag having a strap made of a thin
no further change is observed once the stone
and strong string?
gets fully immersed in the water. What do you
2. What do you mean by buoyancy?
3. Why does an object float or sink
string or the reading of the spring balance?
when placed on the surface of infer from the decrease in the extension of the
water? We know that the elongation produced in
the string or the spring balance is due to the
9.6 Archimedes’ Principle weight of the stone. Since the extension
decreases once the stone is lowered in water,
it means that some force acts on the stone in
Activity ______________ 9.7
upward direction. As a result, the net force on
• Take a piece of stone and tie it to one the string decreases and hence the elongation
end of a rubber string or a spring also decreases. As discussed earlier, this
balance. upward force exerted by water is known as
• Suspend the stone by holding the the force of buoyancy.
balance or the string as shown in What is the magnitude of the buoyant
Fig. 9.6 (a).
• Note the elongation of the string or force experienced by a body? Is it the same
the reading on the spring balance due in all fluids for a given body? Do all bodies
to the weight of the stone. in a given fluid experience the same buoyant
• Now, slowly dip the stone in the water force? The answer to these questions is
in a container as shown in contained in Archimedes’ principle, stated as
Fig. 9.6 (b).
follows:
GRAVITATION 109
Rationalised 2023-24