Page 102 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 102
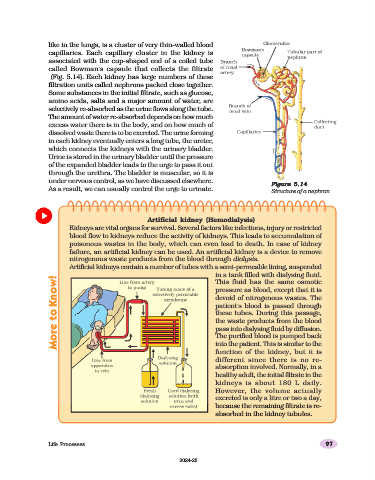
like in the lungs, is a cluster of very thin-walled blood
capillaries. Each capillary cluster in the kidney is
associated with the cup-shaped end of a coiled tube
called Bowman’s capsule that collects the filtrate
(Fig. 5.14). Each kidney has large numbers of these
filtration units called nephrons packed close together.
Some substances in the initial filtrate, such as glucose,
amino acids, salts and a major amount of water, are
selectively re-absorbed as the urine flows along the tube.
The amount of water re-absorbed depends on how much
excess water there is in the body, and on how much of
dissolved waste there is to be excreted. The urine forming
in each kidney eventually enters a long tube, the ureter,
which connects the kidneys with the urinary bladder.
Urine is stored in the urinary bladder until the pressure
of the expanded bladder leads to the urge to pass it out
through the urethra. The bladder is muscular, so it is
under nervous control, as we have discussed elsewhere.
Figure 5.14
Figure 5.14
Figure
Figure 5.145.14
5.14
Figure
As a result, we can usually control the urge to urinate.
Structure of a nephron
Artificial kidney (Hemodialysis)
Kidneys are vital organs for survival. Several factors like infections, injury or restricted
blood flow to kidneys reduce the activity of kidneys. This leads to accumulation of
poisonous wastes in the body, which can even lead to death. In case of kidney
failure, an artificial kidney can be used. An artificial kidney is a device to remove
nitrogenous waste products from the blood through dialysis.
Artificial kidneys contain a number of tubes with a semi-permeable lining, suspended
in a tank filled with dialysing fluid.
More to Know! devoid of nitrogenous wastes. The
This fluid has the same osmotic
pressure as blood, except that it is
patient’s blood is passed through
these tubes. During this passage,
the waste products from the blood
pass into dialysing fluid by diffusion.
The purified blood is pumped back
into the patient. This is similar to the
function of the kidney, but it is
different since there is no re-
absorption involved. Normally, in a
healthy adult, the initial filtrate in the
kidneys is about 180 L daily.
However, the volume actually
excreted is only a litre or two a day,
because the remaining filtrate is re-
absorbed in the kidney tubules.
Life Processes 97
2024-25