Page 106 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 106
object is an urgent and dangerous
situation for us. We need to detect it,
and respond to it. How do we detect that
we are touching a hot object? All
information from our environment is
detected by the specialised tips of some
nerve cells. These receptors are usually
located in our sense organs, such as the
inner ear, the nose, the tongue, and so
(a)
on. So gustatory receptors will detect taste
while olfactory receptors will detect smell.
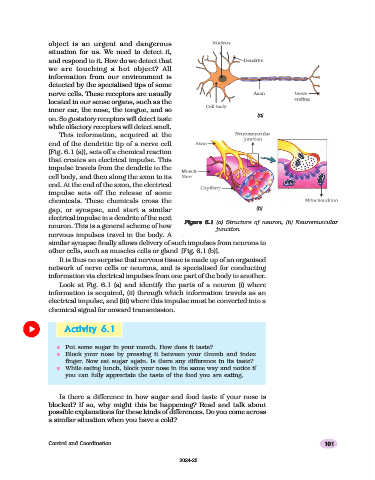
This information, acquired at the
end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell
[Fig. 6.1 (a)], sets off a chemical reaction
that creates an electrical impulse. This
impulse travels from the dendrite to the
cell body, and then along the axon to its
end. At the end of the axon, the electrical
impulse sets off the release of some
chemicals. These chemicals cross the
gap, or synapse, and start a similar (b)
electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next
Figure 6.1 (a) Structure of neuron, (b)
Figure 6.16.1
6.1
Figure 6.1 Neuromuscular
Figure
Figure
neuron. This is a general scheme of how junction
nervous impulses travel in the body. A
similar synapse finally allows delivery of such impulses from neurons to
other cells, such as muscles cells or gland [Fig. 6.1 (b)].
It is thus no surprise that nervous tissue is made up of an organised
network of nerve cells or neurons, and is specialised for conducting
information via electrical impulses from one part of the body to another.
Look at Fig. 6.1 (a) and identify the parts of a neuron (i) where
information is acquired, (ii) through which information travels as an
electrical impulse, and (iii) where this impulse must be converted into a
chemical signal for onward transmission.
Activity
Activity 6.1
6.1
Activity 6.1
Activity 6.16.1
Activity
n Put some sugar in your mouth. How does it taste?
n Block your nose by pressing it between your thumb and index
finger. Now eat sugar again. Is there any difference in its taste?
n While eating lunch, block your nose in the same way and notice if
you can fully appreciate the taste of the food you are eating.
Is there a difference in how sugar and food taste if your nose is
blocked? If so, why might this be happening? Read and talk about
possible explanations for these kinds of differences. Do you come across
a similar situation when you have a cold?
Control and Coordination 101
2024-25