Page 122 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 122
take place in an organised
sequence referred to as
development. However,
regeneration is not the same
as reproduction, since most
organisms would not
normally depend on being cut
up to be able to reproduce.
7.2.4 Budding
Organisms such as Hydra
use regenerative cells for
reproduction in the process of
budding. In Hydra, a bud
Figure
Figure 7.3
Figure 7.37.3
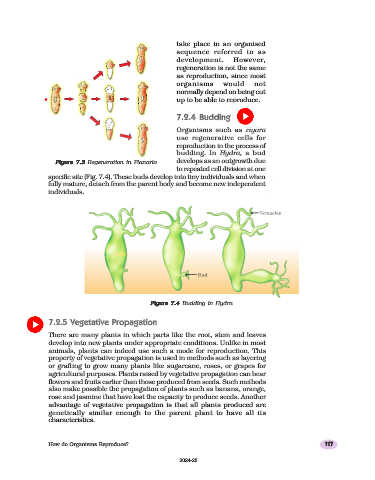
Figure 7.3 Regeneration in Planaria
Figure 7.3 develops as an outgrowth due
to repeated cell division at one
specific site (Fig. 7.4). These buds develop into tiny individuals and when
fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent
individuals.
Figure
Figure
7.4
Figure 7.4 Budding in Hydra
Figure 7.4
Figure 7.47.4
7.2.5 Vegetative Propagation
There are many plants in which parts like the root, stem and leaves
develop into new plants under appropriate conditions. Unlike in most
animals, plants can indeed use such a mode for reproduction. This
property of vegetative propagation is used in methods such as layering
or grafting to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses, or grapes for
agricultural purposes. Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear
flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds. Such methods
also make possible the propagation of plants such as banana, orange,
rose and jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce seeds. Another
advantage of vegetative propagation is that all plants produced are
genetically similar enough to the parent plant to have all its
characteristics.
How do Organisms Reproduce? 117
2024-25