Page 123 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 123
Activity
Activity 7.5
Activity 7.5
Activity 7.57.5
Activity 7.5
n Take a potato and observe its surface. Can notches be seen?
n Cut the potato into small pieces such that some pieces contain a
notch or bud and some do not.
n Spread some cotton on a tray and wet it. Place the potato pieces
on this cotton. Note where the pieces with the buds are placed.
n Observe changes taking place in these potato pieces over the next
few days. Make sure that the cotton is kept moistened.
n Which are the potato pieces that give rise to fresh green shoots
and roots?
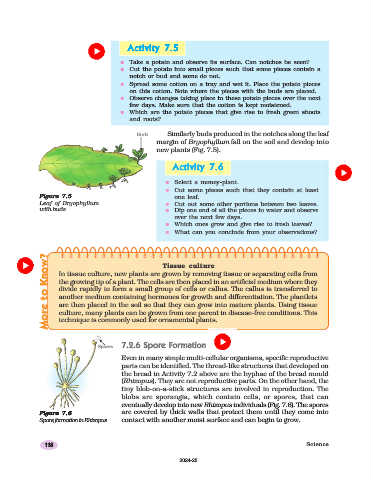
Similarly buds produced in the notches along the leaf
margin of Bryophyllum fall on the soil and develop into
new plants (Fig. 7.5).
Activity
Activity 7.67.6
Activity 7.6
Activity
7.6
Activity 7.6
n Select a money-plant.
n Cut some pieces such that they contain at least
Figure
Figure 7.57.5 one leaf.
7.5
Figure 7.5
Figure 7.5
Figure
Leaf of Bryophyllum n Cut out some other portions between two leaves.
with buds n Dip one end of all the pieces in water and observe
over the next few days.
n Which ones grow and give rise to fresh leaves?
n What can you conclude from your observations?
More to Know? In tissue culture, new plants are grown by removing tissue or separating cells from
Tissue culture
the growing tip of a plant. The cells are then placed in an artificial medium where they
divide rapidly to form a small group of cells or callus. The callus is transferred to
another medium containing hormones for growth and differentiation. The plantlets
are then placed in the soil so that they can grow into mature plants. Using tissue
culture, many plants can be grown from one parent in disease-free conditions. This
technique is commonly used for ornamental plants.
7.2.6 Spore Formation
Even in many simple multi-cellular organisms, specific reproductive
parts can be identified. The thread-like structures that developed on
the bread in Activity 7.2 above are the hyphae of the bread mould
(Rhizopus). They are not reproductive parts. On the other hand, the
tiny blob-on-a-stick structures are involved in reproduction. The
blobs are sporangia, which contain cells, or spores, that can
eventually develop into new Rhizopus individuals (Fig. 7.6). The spores
Figure 7.6
Figure
Figure
Figure 7.6
7.6
Figure 7.67.6 are covered by thick walls that protect them until they come into
Spore formation in Rhizopus contact with another moist surface and can begin to grow.
118 Science
2024-25