Page 16 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 16
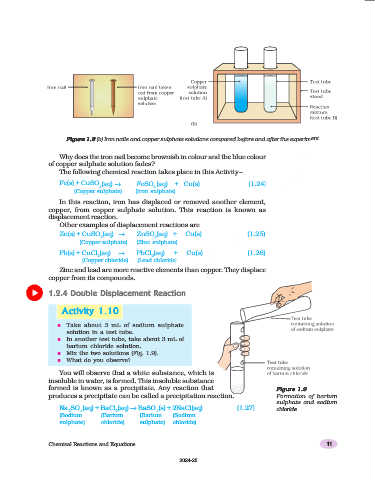
Figure 1.8 (b) Iron nails and copper sulphate solutions compared before and after the experiment
Figure 1.8
Figure 1.8
Figure 1.8
Figure 1.8
Why does the iron nail become brownish in colour and the blue colour
of copper sulphate solution fades?
The following chemical reaction takes place in this Activity–
Fe(s) + CuSO (aq) → FeSO (aq) + Cu(s) (1.24)
4 4
(Copper sulphate) (Iron sulphate)
In this reaction, iron has displaced or removed another element,
copper, from copper sulphate solution. This reaction is known as
displacement reaction.
Other examples of displacement reactions are
Zn(s) + CuSO (aq) → ZnSO (aq) + Cu(s) (1.25)
4 4
(Copper sulphate) (Zinc sulphate)
Pb(s) + CuCl (aq) → PbCl (aq) + Cu(s) (1.26)
2 2
(Copper chloride) (Lead chloride)
Zinc and lead are more reactive elements than copper. They displace
copper from its compounds.
1.2.4 Double Displacement Reaction
Activity 1.101.10
Activity 1.10
Activity 1.10
Activity
Activity 1.10
n Take about 3 mL of sodium sulphate
solution in a test tube.
n In another test tube, take about 3 mL of
barium chloride solution.
n Mix the two solutions (Fig. 1.9).
n What do you observe?
You will observe that a white substance, which is
insoluble in water, is formed. This insoluble substance
formed is known as a precipitate. Any reaction that Figure 1.9
Figure 1.9
Figure 1.9
Figure 1.9
Figure 1.9
produces a precipitate can be called a precipitation reaction. Formation of barium
sulphate and sodium
Na SO (aq) + BaCl (aq) → BaSO (s) + 2NaCl(aq) (1.27) chloride
2 4 2 4
(Sodium (Barium (Barium (Sodium
sulphate) chloride) sulphate) chloride)
Chemical Reactions and Equations 11
2024-25