Page 171 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 171
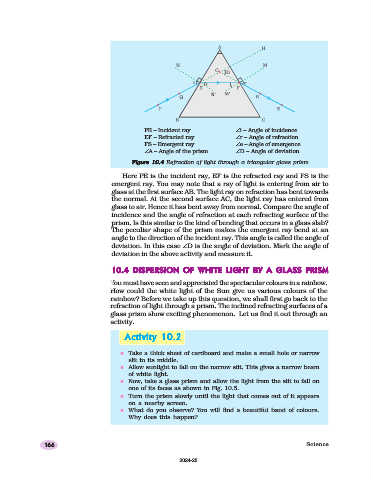
PE – Incident ray ∠i – Angle of incidence
EF – Refracted ray ∠r – Angle of refraction
FS – Emergent ray ∠e – Angle of emergence
∠A – Angle of the prism ∠D – Angle of deviation
Figure 10.4
Figure 10.4 Refraction of light through a triangular glass prism
Figure 10.4
Figure 10.4
Figure 10.4
Here PE is the incident ray, EF is the refracted ray and FS is the
emergent ray. You may note that a ray of light is entering from air to
glass at the first surface AB. The light ray on refraction has bent towards
the normal. At the second surface AC, the light ray has entered from
glass to air. Hence it has bent away from normal. Compare the angle of
incidence and the angle of refraction at each refracting surface of the
prism. Is this similar to the kind of bending that occurs in a glass slab?
The peculiar shape of the prism makes the emergent ray bend at an
angle to the direction of the incident ray. This angle is called the angle of
deviation. In this case ∠D is the angle of deviation. Mark the angle of
deviation in the above activity and measure it.
10.4 DISPERSION OF WHITE LIGHT BY A GLASS PRISMPRISM
LIGHT
WHITE
OF
BY
10.4 DISPERSION
10.4 DISPERSION OF WHITE LIGHT BY A GLASS PRISMASS PRISM
10.4 DISPERSION OF WHITE LIGHT BY A GLDISPERSION OF WHITE LIGHT BY A GLASS PRISM
A
GLASS
10.4
You must have seen and appreciated the spectacular colours in a rainbow.
How could the white light of the Sun give us various colours of the
rainbow? Before we take up this question, we shall first go back to the
refraction of light through a prism. The inclined refracting surfaces of a
glass prism show exciting phenomenon. Let us find it out through an
activity.
10.2
Activity 10.2
Activity 10.2
Activity
Activity 10.210.2
Activity
n Take a thick sheet of cardboard and make a small hole or narrow
slit in its middle.
n Allow sunlight to fall on the narrow slit. This gives a narrow beam
of white light.
n Now, take a glass prism and allow the light from the slit to fall on
one of its faces as shown in Fig. 10.5.
n Turn the prism slowly until the light that comes out of it appears
on a nearby screen.
n What do you observe? You will find a beautiful band of colours.
Why does this happen?
166 Science
2024-25