Page 192 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 192
The current I , through R = V/ R
2 2 2
I = 12 V/10 Ω = 1.2 A.
2
The current I , through R = V/R
3 3 3
I = 12 V/30 Ω = 0.4 A.
3
The total current in the circuit,
I = I + I + I
1 2 3
= (2.4 + 1.2 + 0.4) A
= 4 A
The total resistance R , is given by [Eq. (11.18)]
p
1 1 1 1 1
= + + =
R p 5 10 30 3
Thus, R = 3 Ω.
p
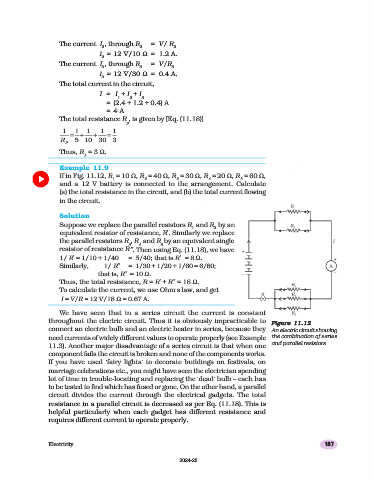
Example 11.9
If in Fig. 11.12, R = 10 Ω, R = 40 Ω, R = 30 Ω, R = 20 Ω, R = 60 Ω,
1 2 3 4 5
and a 12 V battery is connected to the arrangement. Calculate
(a) the total resistance in the circuit, and (b) the total current flowing
in the circuit.
Solution
Suppose we replace the parallel resistors R and R by an
1 2
equivalent resistor of resistance, R′. Similarly we replace
the parallel resistors R , R and R by an equivalent single
3 4 5
resistor of resistance R″. Then using Eq. (11.18), we have
1/ R′ = 1/10 + 1/40 = 5/40; that is R′ = 8 Ω.
Similarly, 1/ R″ = 1/30 + 1/20 + 1/60 = 6/60;
that is, R″ = 10 Ω.
Thus, the total resistance, R = R′ + R″ = 18 Ω.
To calculate the current, we use Ohm’s law, and get
I = V/R = 12 V/18 Ω = 0.67 A.
We have seen that in a series circuit the current is constant
throughout the electric circuit. Thus it is obviously impracticable to Figure 11.12
Figure
Figure
11.12
Figure 11.1211.12
Figure 11.12
connect an electric bulb and an electric heater in series, because they An electric circuit showing
need currents of widely different values to operate properly (see Example the combination of series
11.3). Another major disadvantage of a series circuit is that when one and parallel resistors
component fails the circuit is broken and none of the components works.
If you have used ‘fairy lights’ to decorate buildings on festivals, on
marriage celebrations etc., you might have seen the electrician spending
lot of time in trouble-locating and replacing the ‘dead’ bulb – each has
to be tested to find which has fused or gone. On the other hand, a parallel
circuit divides the current through the electrical gadgets. The total
resistance in a parallel circuit is decreased as per Eq. (11.18). This is
helpful particularly when each gadget has different resistance and
requires different current to operate properly.
Electricity 187
2024-25