Page 188 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 188
Activity 11.511.5
Activity 11.5
Activity 11.5
Activity
Activity 11.5
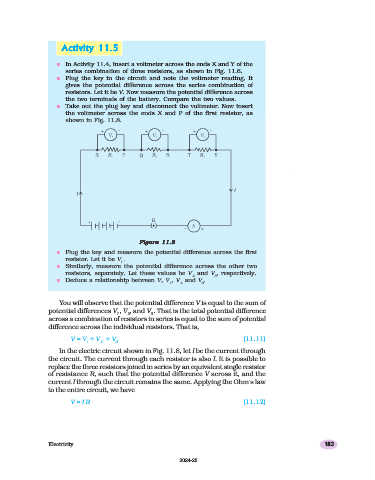
n In Activity 11.4, insert a voltmeter across the ends X and Y of the
series combination of three resistors, as shown in Fig. 11.6.
n Plug the key in the circuit and note the voltmeter reading. It
gives the potential difference across the series combination of
resistors. Let it be V. Now measure the potential difference across
the two terminals of the battery. Compare the two values.
n Take out the plug key and disconnect the voltmeter. Now insert
the voltmeter across the ends X and P of the first resistor, as
shown in Fig. 11.8.
Figure 11.811.8
Figure 11.8
Figure 11.8
11.8
Figure
Figure
n Plug the key and measure the potential difference across the first
resistor. Let it be V .
1
n Similarly, measure the potential difference across the other two
resistors, separately. Let these values be V and V , respectively.
2 3
n Deduce a relationship between V, V , V and V .
1 2 3
You will observe that the potential difference V is equal to the sum of
potential differences V , V , and V . That is the total potential difference
1 2 3
across a combination of resistors in series is equal to the sum of potential
difference across the individual resistors. That is,
V = V + V + V (11.11)
1 2 3
In the electric circuit shown in Fig. 11.8, let I be the current through
the circuit. The current through each resistor is also I. It is possible to
replace the three resistors joined in series by an equivalent single resistor
of resistance R, such that the potential difference V across it, and the
current I through the circuit remains the same. Applying the Ohm’s law
to the entire circuit, we have
V = I R (11.12)
Electricity 183
2024-25