Page 44 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 44
Activity 3.6
Activity
Activity 3.63.6
Activity 3.6
3.6
Activity
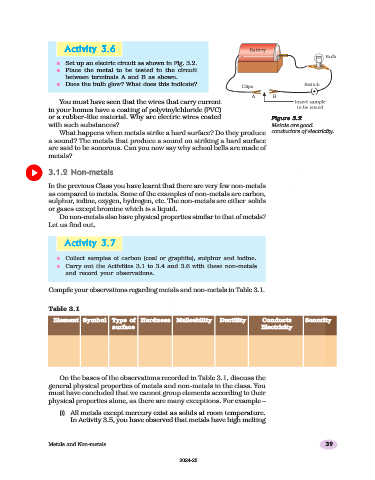
n Set up an electric circuit as shown in Fig. 3.2.
n Place the metal to be tested in the circuit
between terminals A and B as shown.
n Does the bulb glow? What does this indicate?
You must have seen that the wires that carry current
in your homes have a coating of polyvinylchloride (PVC)
or a rubber-like material. Why are electric wires coated Figure 3.2
Figure 3.2
Figure 3.2
Figure 3.2
Figure 3.2
with such substances? Metals are good
What happens when metals strike a hard surface? Do they produce conductors of electricity.
a sound? The metals that produce a sound on striking a hard surface
are said to be sonorous. Can you now say why school bells are made of
metals?
3.1.2 Non-metals
In the previous Class you have learnt that there are very few non-metals
as compared to metals. Some of the examples of non-metals are carbon,
sulphur, iodine, oxygen, hydrogen, etc. The non-metals are either solids
or gases except bromine which is a liquid.
Do non-metals also have physical properties similar to that of metals?
Let us find out.
Activity 3.7
Activity 3.73.7
Activity 3.7
Activity
Activity 3.7
n Collect samples of carbon (coal or graphite), sulphur and iodine.
n Carry out the Activities 3.1 to 3.4 and 3.6 with these non-metals
and record your observations.
Compile your observations regarding metals and non-metals in Table 3.1.
Table 3.1
Element Symbol Type of Hardness Malleability Ductility Conducts Sonority
surface Electricity
On the bases of the observations recorded in Table 3.1, discuss the
general physical properties of metals and non-metals in the class. You
must have concluded that we cannot group elements according to their
physical properties alone, as there are many exceptions. For example –
(i) All metals except mercury exist as solids at room temperature.
In Activity 3.5, you have observed that metals have high melting
Metals and Non-metals 39
2024-25