Page 58 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 58
metal from the electrolyte is deposited on the cathode. The soluble
impurities go into the solution, whereas, the insoluble impurities settle
down at the bottom of the anode and are known as anode mud.
Q U E S T I O N S
1. Define the following terms.
(i) Mineral (ii) Ore (iii) Gangue
2. Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state. ?
3. What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
3.5 CORROSION
3.5 CORROSIONCORROSION
3.5 CORROSION
3.5 CORROSION
3.5
You have learnt the following about corrosion in Chapter 1 –
n Silver articles become black after some time when exposed to air.
This is because it reacts with sulphur in the air to form a coating
of silver sulphide.
n Copper reacts with moist carbon dioxide in the air and slowly loses
its shiny brown surface and gains a green coat. This green
substance is basic copper carbonate.
n Iron when exposed to moist air for a long time acquires a coating
of a brown flaky substance called rust.
Let us find out the conditions under which iron rusts.
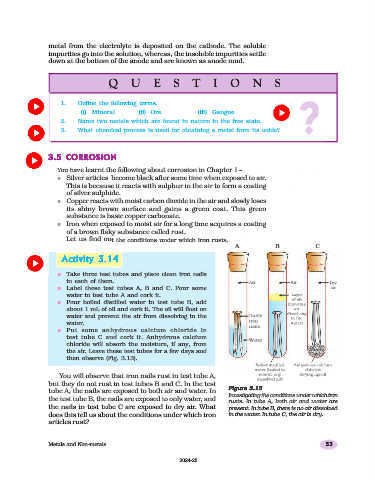
A B C
Activity 3.14
Activity
Activity 3.14
3.14
Activity
Activity 3.143.14
n Take three test tubes and place clean iron nails
in each of them.
n Label these test tubes A, B and C. Pour some
water in test tube A and cork it.
n Pour boiled distilled water in test tube B, add
about 1 mL of oil and cork it. The oil will float on
water and prevent the air from dissolving in the
water.
n Put some anhydrous calcium chloride in
test tube C and cork it. Anhydrous calcium
chloride will absorb the moisture, if any, from
the air. Leave these test tubes for a few days and
then observe (Fig. 3.13).
You will observe that iron nails rust in test tube A,
but they do not rust in test tubes B and C. In the test
Figure 3.13
Figure 3.13
Figure 3.13
Figure 3.13
tube A, the nails are exposed to both air and water. In Figure 3.13
Investigating the conditions under which iron
the test tube B, the nails are exposed to only water, and rusts. In tube A, both air and water are
the nails in test tube C are exposed to dry air. What present. In tube B, there is no air dissolved
does this tell us about the conditions under which iron in the water. In tube C, the air is dry.
articles rust?
Metals and Non-metals 53
2024-25