Page 53 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 53
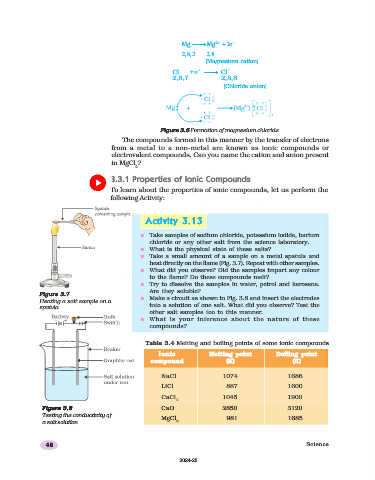
Mg → Mg 2+ + 2 e –
,
,
2 8 2 2 8
,
(Magnesium cation)
Cl +e – → Cl –
2,8,7 2,8,8
(Chloride anion)
Figure 3.6
Figure 3.6
Figure 3.6
Figure 3.6
Figure 3.6 Formation of magnesium chloride
The compounds formed in this manner by the transfer of electrons
from a metal to a non-metal are known as ionic compounds or
electrovalent compounds. Can you name the cation and anion present
in MgCl ?
2
3.3.1 Properties of Ionic Compounds
To learn about the properties of ionic compounds, let us perform the
following Activity:
Activity 3.13
Activity
Activity 3.133.13
3.13
Activity
Activity 3.13
n Take samples of sodium chloride, potassium iodide, barium
chloride or any other salt from the science laboratory.
n What is the physical state of these salts?
n Take a small amount of a sample on a metal spatula and
heat directly on the flame (Fig. 3.7). Repeat with other samples.
n What did you observe? Did the samples impart any colour
to the flame? Do these compounds melt?
n Try to dissolve the samples in water, petrol and kerosene.
Are they soluble?
Figure 3.7
Figure 3.7
Figure 3.7
Figure 3.7
Figure 3.7
Heating a salt sample on a n Make a circuit as shown in Fig. 3.8 and insert the electrodes
spatula into a solution of one salt. What did you observe? Test the
other salt samples too in this manner.
n What is your inference about the nature of these
compounds?
Table 3.4 Melting and boiling points of some ionic compounds
Ionic Melting point Boiling point
compound (K) (K)
NaCl 1074 1686
LiCl 887 1600
CaCl 1045 1900
2
Figure 3.8
Figure 3.8
Figure 3.8 CaO 2850 3120
Figure 3.8
Figure 3.8
Testing the conductivity of
MgCl 981 1685
a salt solution 2
48 Science
2024-25