Page 88 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 88
Now, let us study how the plant
obtains carbon dioxide. In Class IX,
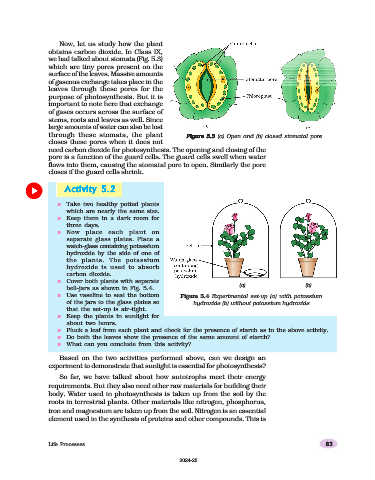
we had talked about stomata (Fig. 5.3)
which are tiny pores present on the
surface of the leaves. Massive amounts
of gaseous exchange takes place in the
leaves through these pores for the
purpose of photosynthesis. But it is
important to note here that exchange
of gases occurs across the surface of
stems, roots and leaves as well. Since
large amounts of water can also be lost
through these stomata, the plant Figure 5.3
Figure 5.3 (a) Open and (b) closed stomatal pore
Figure 5.3
Figure 5.3
Figure 5.3
closes these pores when it does not
need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The opening and closing of the
pore is a function of the guard cells. The guard cells swell when water
flows into them, causing the stomatal pore to open. Similarly the pore
closes if the guard cells shrink.
Activity 5.25.2
Activity 5.2
Activity 5.2
Activity 5.2
Activity
n Take two healthy potted plants
which are nearly the same size.
n Keep them in a dark room for
three days.
n Now place each plant on
separate glass plates. Place a
watch-glass containing potassium
hydroxide by the side of one of
the plants. The potassium
hydroxide is used to absorb
carbon dioxide.
n Cover both plants with separate
(a) (b)
bell-jars as shown in Fig. 5.4.
n Use vaseline to seal the bottom Figure 5.4 Experimental set-up (a) with potassium
of the jars to the glass plates so hydroxide (b) without potassium hydroxide
that the set-up is air-tight.
n Keep the plants in sunlight for
about two hours.
n Pluck a leaf from each plant and check for the presence of starch as in the above activity.
n Do both the leaves show the presence of the same amount of starch?
n What can you conclude from this activity?
Based on the two activities performed above, can we design an
experiment to demonstrate that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis?
So far, we have talked about how autotrophs meet their energy
requirements. But they also need other raw materials for building their
body. Water used in photosynthesis is taken up from the soil by the
roots in terrestrial plants. Other materials like nitrogen, phosphorus,
iron and magnesium are taken up from the soil. Nitrogen is an essential
element used in the synthesis of proteins and other compounds. This is
Life Processes 83
2024-25