Page 92 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 92
Q U E S T I O N S
1. What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic
nutrition?
2. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
3. What is the role of the acid in our stomach? ?
4. What is the function of digestive enzymes?
5. How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
5.3 RESPIRATION
5.3
5.3 RESPIRRESPIRATIONTION
5.3
RESPIR
5.3 RESPIRAA ATIONTION
Pichkari
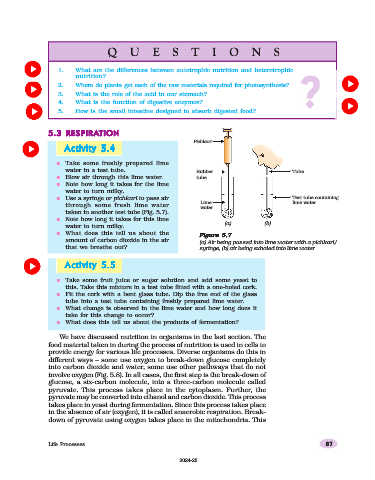
Activity 5.4
Activity 5.4
Activity 5.45.4
Activity 5.4
Activity
n Take some freshly prepared lime
water in a test tube. Rubber Tube
n Blow air through this lime water. tube
n Note how long it takes for the lime
water to turn milky.
n Use a syringe or pichkari to pass air Test tube containing
through some fresh lime water Lime lime water
water
taken in another test tube (Fig. 5.7).
n Note how long it takes for this lime
(a) (b)
water to turn milky.
n What does this tell us about the Figure 5.7
Figure 5.75.7
Figure
Figure 5.7
5.7
Figure
amount of carbon dioxide in the air (a) Air being passed into lime water with a pichkari/
that we breathe out? syringe, (b) air being exhaled into lime water
Activity
Activity 5.55.5
Activity 5.5
5.5
Activity 5.5
Activity
n Take some fruit juice or sugar solution and add some yeast to
this. Take this mixture in a test tube fitted with a one-holed cork.
n Fit the cork with a bent glass tube. Dip the free end of the glass
tube into a test tube containing freshly prepared lime water.
n What change is observed in the lime water and how long does it
take for this change to occur?
n What does this tell us about the products of fermentation?
We have discussed nutrition in organisms in the last section. The
food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used in cells to
provide energy for various life processes. Diverse organisms do this in
different ways – some use oxygen to break-down glucose completely
into carbon dioxide and water, some use other pathways that do not
involve oxygen (Fig. 5.8). In all cases, the first step is the break-down of
glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called
pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm. Further, the
pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process
takes place in yeast during fermentation. Since this process takes place
in the absence of air (oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration. Break-
down of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the mitochondria. This
Life Processes 87
2024-25