Page 28 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 28
(ii) Mass by volume percentage of a solution • The particles of a suspension scatter a
beam of light passing through it and
Mass of solute
= ×100 make its path visible.
Volume of solution
• The solute particles settle down when a
(iii) Volume by volume percentage of a suspension is left undisturbed, that is,
solution a suspension is unstable. They can be
separated from the mixture by the
Volume of solute
= ×100 process of filtration. When the particles
Volume of solution
settle down, the suspension breaks and
it does not scatter light any more.
Example 2.1 A solution contains 40 g of
common salt in 320 g of water. Calculate
the concentration in terms of mass by 2.2.3 WHAT IS A COLLOIDAL SOLUTION?
mass percentage of the solution. The mixture obtained by group D in activity
Solution: 2.2 is called a colloid or a colloidal solution.
The particles of a colloid are uniformly spread
Mass of solute (salt) = 40 g
Mass of solvent (water) = 320 g throughout the solution. Due to the relatively
We know, smaller size of particles, as compared to that of
Mass of solution = Mass of solute + a suspension, the mixture appears to be
Mass of solvent homogeneous. But actually, a colloidal solution
= 40 g + 320 g is a heterogeneous mixture, for example, milk.
= 360 g Because of the small size of colloidal
particles, we cannot see them with naked eyes.
Mass percentage of solution
But, these particles can easily scatter a beam
Mass of solute of visible light as observed in activity 2.2. This
= ×100
Massof solution scattering of a beam of light is called the
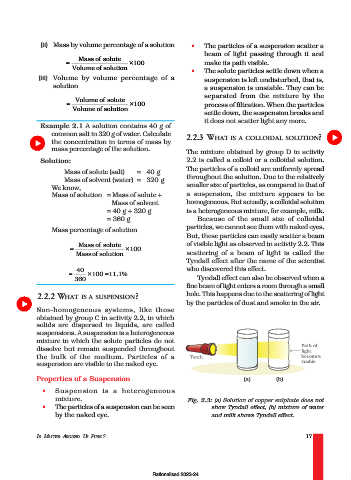
Tyndall effect after the name of the scientist
40 who discovered this effect.
= ×100 =11.1% Tyndall effect can also be observed when a
360
fine beam of light enters a room through a small
2.2.2 WHAT IS A SUSPENSION? hole. This happens due to the scattering of light
by the particles of dust and smoke in the air.
Non-homogeneous systems, like those
obtained by group C in activity 2.2, in which
solids are dispersed in liquids, are called
suspensions. A suspension is a heterogeneous
mixture in which the solute particles do not
dissolve but remain suspended throughout
the bulk of the medium. Particles of a
suspension are visible to the naked eye.
Properties of a Suspension (a) (b)
• Suspension is a heterogeneous
mixture. Fig. 2.3: (a) Solution of copper sulphate does not
• The particles of a suspension can be seen show Tyndall effect, (b) mixture of water
by the naked eye. and milk shows Tyndall effect.
IS MATTER AROUND US PURE? 17
Rationalised 2023-24