Page 29 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 29
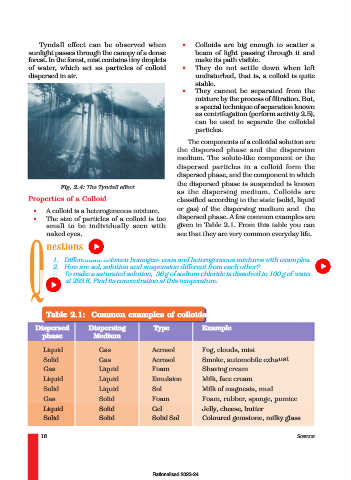
Tyndall effect can be observed when • Colloids are big enough to scatter a
sunlight passes through the canopy of a dense beam of light passing through it and
forest. In the forest, mist contains tiny droplets make its path visible.
of water, which act as particles of colloid • They do not settle down when left
dispersed in air. undisturbed, that is, a colloid is quite
stable.
• They cannot be separated from the
mixture by the process of filtration. But,
a special technique of separation known
as centrifugation (perform activity 2.5),
can be used to separate the colloidal
particles.
The components of a colloidal solution are
the dispersed phase and the dispersion
medium. The solute-like component or the
dispersed particles in a colloid form the
dispersed phase, and the component in which
the dispersed phase is suspended is known
Fig. 2.4: The Tyndall effect
as the dispersing medium. Colloids are
Properties of a Colloid classified according to the state (solid, liquid
• A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture. or gas) of the dispersing medium and the
• The size of particles of a colloid is too dispersed phase. A few common examples are
small to be individually seen with given in Table 2.1. From this table you can
naked eyes. see that they are very common everyday life.
Q 1. Differentiate between homogen- eous and heterogeneous mixtures with examples.
uestions
2. How are sol, solution and suspension different from each other?
3. To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water
at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Table 2.1: Common examples of colloids
Dispersed Dispersing Type Example
phase Medium
Liquid Gas Aerosol Fog, clouds, mist
Solid Gas Aerosol Smoke, automobile exhaust
Gas Liquid Foam Shaving cream
Liquid Liquid Emulsion Milk, face cream
Solid Liquid Sol Milk of magnesia, mud
Gas Solid Foam Foam, rubber, sponge, pumice
Liquid Solid Gel Jelly, cheese, butter
Solid Solid Solid Sol Coloured gemstone, milky glass
18 SCIENCE
Rationalised 2023-24