Page 50 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 50
Q uestions J.J. Thomson (1856–
a
1940),
British
1. What are canal rays?
physicist, was born in
2. If an atom contains one electron
Cheetham Hill, a suburb
and one proton, will it carry any
Manchester,
of
on
charge or not?
18 December 1856. He
was awarded the Nobel
prize in Physics in 1906
for his work on the
4.2 The Structure of an Atom discovery of electrons. He
directed the Cavendish Laboratory at
We have learnt Dalton’s atomic theory in Cambridge for 35 years and seven of his
Chapter 3, which suggested that the atom research assistants subsequently won
was indivisible and indestructible. But the Nobel prizes.
discovery of two fundamental particles
(electrons and protons) inside the atom, led Thomson proposed that:
to the failure of this aspect of Dalton’s atomic (i) An atom consists of a positively
theory. It was then considered necessary to charged sphere and the electrons are
know how electrons and protons are arranged embedded in it.
within an atom. For explaining this, many (ii) The negative and positive charges are
scientists proposed various atomic models. equal in magnitude. So, the atom as a
J.J. Thomson was the first one to propose a whole is electrically neutral.
model for the structure of an atom.
Although Thomson’s model explained that
atoms are electrically neutral, the results of
4.2.1 THOMSON’S MODEL OF AN ATOM
experiments carried out by other scientists
could not be explained by this model, as we
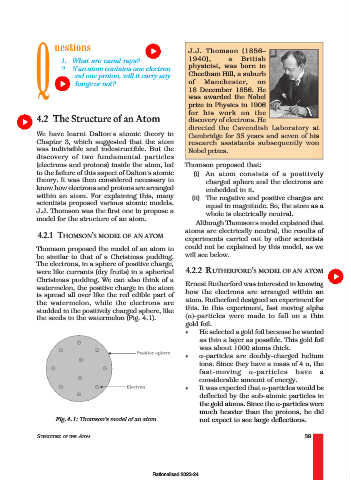
Thomson proposed the model of an atom to
be similar to that of a Christmas pudding. will see below.
The electrons, in a sphere of positive charge,
were like currants (dry fruits) in a spherical 4.2.2 RUTHERFORD’S MODEL OF AN ATOM
Christmas pudding. We can also think of a
Ernest Rutherford was interested in knowing
watermelon, the positive charge in the atom
is spread all over like the red edible part of how the electrons are arranged within an
the watermelon, while the electrons are atom. Rutherford designed an experiment for
studded in the positively charged sphere, like this. In this experiment, fast moving alpha
the seeds in the watermelon (Fig. 4.1). (α)-particles were made to fall on a thin
gold foil.
• He selected a gold foil because he wanted
as thin a layer as possible. This gold foil
was about 1000 atoms thick.
• α-particles are doubly-charged helium
ions. Since they have a mass of 4 u, the
fast-moving α-particles have a
considerable amount of energy.
• It was expected that α-particles would be
deflected by the sub-atomic particles in
the gold atoms. Since the α-particles were
much heavier than the protons, he did
Fig.4.1: Thomson’s model of an atom not expect to see large deflections.
STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM 39
Rationalised 2023-24