Page 177 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 177
If a net charge Q, flows across any cross-section of a conductor in
time t, then the current I, through the cross-section is
Q
I = (11.1)
t
The SI unit of electric charge is coulomb (C), which is equivalent to
the charge contained in nearly 6 × 10 electrons. (We know that an
18
electron possesses a negative charge of 1.6 × 10 –19 C.) The electric
current is expressed by a unit called ampere (A), named after the
French scientist, Andre-Marie Ampere (1775–1836). One ampere is
constituted by the flow of one coulomb of charge per second, that is,
1 A = 1 C/1 s. Small quantities of current are expressed in milliampere
–6
–3
(1 mA = 10 A) or in microampere (1 µA = 10 A).
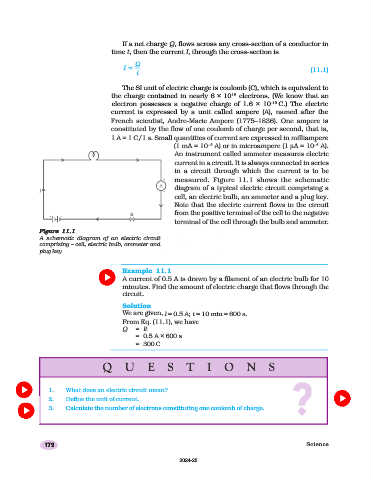
An instrument called ammeter measures electric
current in a circuit. It is always connected in series
in a circuit through which the current is to be
measured. Figure 11.1 shows the schematic
diagram of a typical electric circuit comprising a
cell, an electric bulb, an ammeter and a plug key.
Note that the electric current flows in the circuit
from the positive terminal of the cell to the negative
terminal of the cell through the bulb and ammeter.
Figure 11.111.1
Figure
Figure 11.1
Figure 11.1
11.1
Figure
A schematic diagram of an electric circuit
comprising – cell, electric bulb, ammeter and
plug key
Example 11.1
A current of 0.5 A is drawn by a filament of an electric bulb for 10
minutes. Find the amount of electric charge that flows through the
circuit.
Solution
We are given, I = 0.5 A; t = 10 min = 600 s.
From Eq. (11.1), we have
Q = It
= 0.5 A × 600 s
= 300 C
Q U E S T I O N S
?
1. What does an electric circuit mean?
2. Define the unit of current.
3. Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
172 Science
2024-25