Page 208 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 208
the direction of force acting on the current-carrying rod gets reversed. It
shows that the direction of the force on the conductor depends upon the
direction of current and the direction of the magnetic field. Experiments
have shown that the displacement of the rod is largest (or the magnitude
of the force is the highest) when the direction of current is at right angles
to the direction of the magnetic field. In such a condition we can use a
simple rule to find the direction of the force on the conductor.
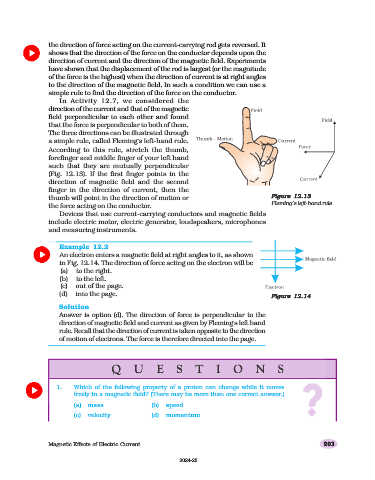
In Activity 12.7, we considered the
direction of the current and that of the magnetic
field perpendicular to each other and found
that the force is perpendicular to both of them.
The three directions can be illustrated through
a simple rule, called Fleming’s left-hand rule.
According to this rule, stretch the thumb,
forefinger and middle finger of your left hand
such that they are mutually perpendicular
(Fig. 12.13). If the first finger points in the
direction of magnetic field and the second
finger in the direction of current, then the
Figure
Figure
Figure 12.13
Figure 12.13
12.13
thumb will point in the direction of motion or Figure 12.1312.13
Fleming’s left-hand rule
the force acting on the conductor.
Devices that use current-carrying conductors and magnetic fields
include electric motor, electric generator, loudspeakers, microphones
and measuring instruments.
Example 12.2
An electron enters a magnetic field at right angles to it, as shown
in Fig. 12.14. The direction of force acting on the electron will be
(a) to the right.
(b) to the left.
(c) out of the page.
(d) into the page. Figure 12.14
Figure 12.1412.14
Figure 12.14
Figure
12.14
Figure
Solution
Answer is option (d). The direction of force is perpendicular to the
direction of magnetic field and current as given by Fleming’s left hand
rule. Recall that the direction of current is taken opposite to the direction
of motion of electrons. The force is therefore directed into the page.
Q U E S T I O N S
1. Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves
freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
(a) mass (b) speed ?
(c) velocity (d) momentum
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current 203
2024-25