Page 80 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 80
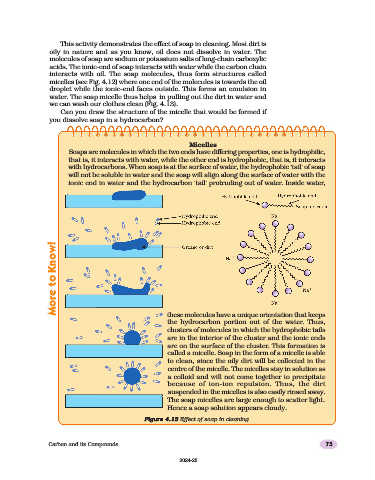
This activity demonstrates the effect of soap in cleaning. Most dirt is
oily in nature and as you know, oil does not dissolve in water. The
molecules of soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic
acids. The ionic-end of soap interacts with water while the carbon chain
interacts with oil. The soap molecules, thus form structures called
micelles (see Fig. 4.12) where one end of the molecules is towards the oil
droplet while the ionic-end faces outside. This forms an emulsion in
water. The soap micelle thus helps in pulling out the dirt in water and
we can wash our clothes clean (Fig. 4.13).
Can you draw the structure of the micelle that would be formed if
you dissolve soap in a hydrocarbon?
Micelles
Soaps are molecules in which the two ends have differing properties, one is hydrophilic,
that is, it interacts with water, while the other end is hydrophobic, that is, it interacts
with hydrocarbons. When soap is at the surface of water, the hydrophobic ‘tail’ of soap
will not be soluble in water and the soap will align along the surface of water with the
ionic end in water and the hydrocarbon ‘tail’ protruding out of water. Inside water,
More to Know!
these molecules have a unique orientation that keeps
the hydrocarbon portion out of the water. Thus,
clusters of molecules in which the hydrophobic tails
are in the interior of the cluster and the ionic ends
are on the surface of the cluster. This formation is
called a micelle. Soap in the form of a micelle is able
to clean, since the oily dirt will be collected in the
centre of the micelle. The micelles stay in solution as
a colloid and will not come together to precipitate
because of ion-ion repulsion. Thus, the dirt
suspended in the micelles is also easily rinsed away.
The soap micelles are large enough to scatter light.
Hence a soap solution appears cloudy.
Figure 4.13 Effect of soap in cleaning
Figure 4.13
Figure 4.13
Figure 4.13
Figure 4.13
Carbon and its Compounds 75
2024-25