Page 158 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 158
Activity
Activity 9.139.13
Activity 9.13
Activity 9.13
Activity 9.13
n Take a concave lens. Place it on a lens stand.
n Place a burning candle on one side of the lens.
n Look through the lens from the other side and observe the image.
Try to get the image on a screen, if possible. If not, observe the
image directly through the lens.
n Note down the nature, relative size and approximate position of
the image.
n Move the candle away from the lens. Note the change in the size
of the image. What happens to the size of the image when the
candle is placed too far away from the lens.
The summary of the above Activity is given in Table 9.5 below.
Table 9.5 Nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a concave lens for various
positions of the object
Position of the Position of Relative size of Nature of
object the image the image the image
At infinity At focus F Highly diminished, Virtual and erect
1
point-sized
Between infinity and Between focus F Diminished Virtual and erect
1
optical centre O and optical centre O
of the lens
What conclusion can you draw from this Activity? A concave lens
will always give a virtual, erect and diminished image, irrespective of the
position of the object.
9.3.5 Image Formation in Lenses Using Ray Diagrams
We can represent image formation by lenses using ray diagrams. Ray
diagrams will also help us to study the nature, position and relative size
of the image formed by lenses. For drawing ray diagrams in lenses, alike
of spherical mirrors, we consider any two of the following rays –
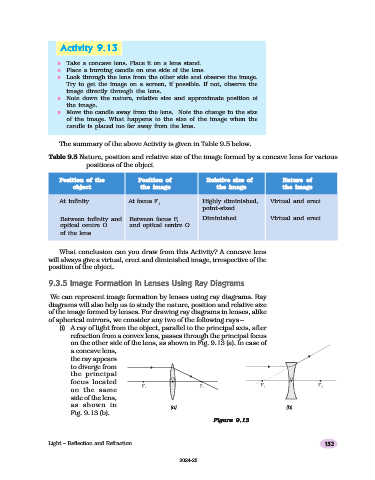
(i) A ray of light from the object, parallel to the principal axis, after
refraction from a convex lens, passes through the principal focus
on the other side of the lens, as shown in Fig. 9.13 (a). In case of
a concave lens,
the ray appears
to diverge from
the principal
focus located
on the same
side of the lens,
as shown in
(a) (b)
Fig. 9.13 (b).
Figure 9.13
Figure
Figure 9.13
Figure 9.139.13
Figure 9.13
Light – Reflection and Refraction 153
2024-25