Page 155 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 155
Q U E S T I O N S
1. A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light
ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal? Why?
2. Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the
8
–1
speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 10 m s .
3. Find out, from Table 9.3, the medium having highest optical density. ?
Also find the medium with lowest optical density.
4. You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does
the light travel fastest? Use the information given in Table 9.3.
5. The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this
statement?
9.3.3 Refraction by Spherical Lenses
You might have seen watchmakers using a small magnifying glass to
see tiny parts. Have you ever touched the surface of a magnifying glass
with your hand? Is it plane surface or curved? Is it thicker in the middle
or at the edges? The glasses used in spectacles and that by a watchmaker
are examples of lenses. What is a lens? How does it bend light rays? We
shall discuss these in this section.
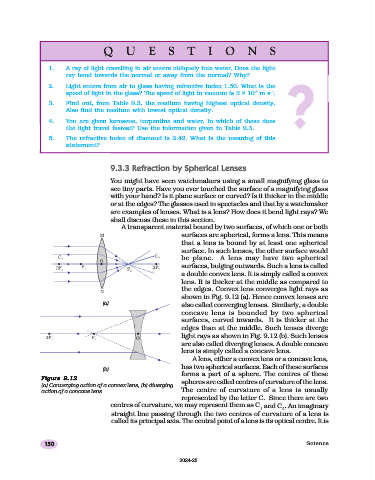
A transparent material bound by two surfaces, of which one or both
surfaces are spherical, forms a lens. This means
that a lens is bound by at least one spherical
surface. In such lenses, the other surface would
be plane. A lens may have two spherical
surfaces, bulging outwards. Such a lens is called
a double convex lens. It is simply called a convex
lens. It is thicker at the middle as compared to
the edges. Convex lens converges light rays as
shown in Fig. 9.12 (a). Hence convex lenses are
(a)
also called converging lenses. Similarly, a double
concave lens is bounded by two spherical
surfaces, curved inwards. It is thicker at the
edges than at the middle. Such lenses diverge
light rays as shown in Fig. 9.12 (b). Such lenses
are also called diverging lenses. A double concave
lens is simply called a concave lens.
A lens, either a convex lens or a concave lens,
(b) has two spherical surfaces. Each of these surfaces
forms a part of a sphere. The centres of these
Figure 9.12
Figure
Figure 9.129.12
Figure 9.12
Figure 9.12
(a) Converging action of a convex lens, (b) diverging spheres are called centres of curvature of the lens.
action of a concave lens The centre of curvature of a lens is usually
represented by the letter C. Since there are two
centres of curvature, we may represent them as C and C . An imaginary
1 2
straight line passing through the two centres of curvature of a lens is
called its principal axis. The central point of a lens is its optical centre. It is
150 Science
2024-25