Page 153 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 153
The following are the laws of refraction of light.
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface
of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the
same plane.
(ii) The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of
refraction is a constant, for the light of a given colour and for
the given pair of media. This law is also known as Snell’s law of
o
refraction. (This is true for angle 0 < i < 90 )
If i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction, then,
sini
= constant (9.4)
sinr
This constant value is called the refractive index of the second medium
with respect to the first. Let us study about refractive index in some detail.
9.3.2 The Refractive Index
You have already studied that a ray of light that travels obliquely from
one transparent medium into another will change its direction in the
second medium. The extent of the change in direction that takes place
in a given pair of media may be expressed in terms of the refractive index,
the “constant” appearing on the right-hand side of Eq.(9.4).
The refractive index can be linked to an important physical quantity,
the relative speed of propagation of light in different media. It turns
out that light propagates with different speeds in different media. Light
travels fastest in vacuum with speed of 3×10 m s . In air, the speed of
8
–1
light is only marginally less, compared to that in vacuum. It reduces
considerably in glass or water. The value of the refractive index for a
given pair of media depends upon the speed of light in the two media, as
given below.
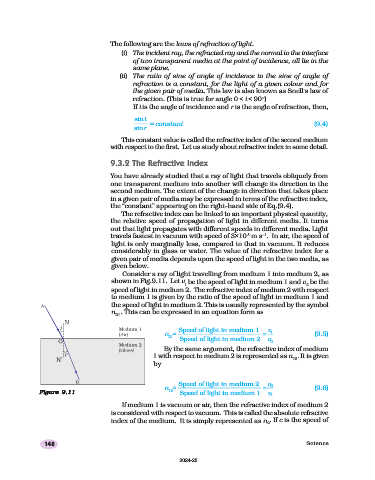
Consider a ray of light travelling from medium 1 into medium 2, as
shown in Fig.9.11. Let v be the speed of light in medium 1 and v be the
1 2
speed of light in medium 2. The refractive index of medium 2 with respect
to medium 1 is given by the ratio of the speed of light in medium 1 and
the speed of light in medium 2. This is usually represented by the symbol
n . This can be expressed in an equation form as
21
Speed of light in medium 1 v
n = = 1 (9.5)
21 Speed of light in medium 2 v 2
By the same argument, the refractive index of medium
1 with respect to medium 2 is represented as n .It is given
12
by
Speed of light in medium 2 v
n = = 2 (9.6)
Figure
Figure 9.11 12 Speed of light in medium 1 v
Figure 9.11
Figure 9.119.11
Figure 9.11
1
If medium 1 is vacuum or air, then the refractive index of medium 2
is considered with respect to vacuum. This is called the absolute refractive
index of the medium. It is simply represented as n . If c is the speed of
2
148 Science
2024-25