Page 154 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 154
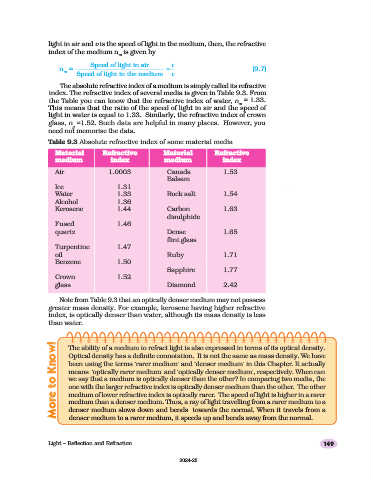
light in air and v is the speed of light in the medium, then, the refractive
index of the medium n is given by
m
Speed of light in air c
n = = (9.7)
m
Speed of light in the medium v
The absolute refractive index of a medium is simply called its refractive
index. The refractive index of several media is given in Table 9.3. From
the Table you can know that the refractive index of water, n = 1.33.
w
This means that the ratio of the speed of light in air and the speed of
light in water is equal to 1.33. Similarly, the refractive index of crown
glass, n =1.52. Such data are helpful in many places. However, you
g
need not memorise the data.
Table 9.3 Absolute refractive index of some material media
Material Refractive Material Refractive
medium index medium index
Air 1.0003 Canada 1.53
Balsam
Ice 1.31
Water 1.33 Rock salt 1.54
Alcohol 1.36
Kerosene 1.44 Carbon 1.63
disulphide
Fused 1.46
quartz Dense 1.65
flint glass
Turpentine 1.47
oil Ruby 1.71
Benzene 1.50
Sapphire 1.77
Crown 1.52
glass Diamond 2.42
Note from Table 9.3 that an optically denser medium may not possess
greater mass density. For example, kerosene having higher refractive
index, is optically denser than water, although its mass density is less
than water.
More to Know! Optical density has a definite connotation. It is not the same as mass density. We have
The ability of a medium to refract light is also expressed in terms of its optical density.
been using the terms ‘rarer medium’ and ‘denser medium’ in this Chapter. It actually
means ‘optically rarer medium’ and ‘optically denser medium’, respectively. When can
we say that a medium is optically denser than the other? In comparing two media, the
one with the larger refractive index is optically denser medium than the other. The other
medium of lower refractive index is optically rarer. The speed of light is higher in a rarer
medium than a denser medium. Thus, a ray of light travelling from a rarer medium to a
denser medium slows down and bends towards the normal. When it travels from a
denser medium to a rarer medium, it speeds up and bends away from the normal.
Light – Reflection and Refraction 149
2024-25