Page 68 - NCERT Science Class 10 English Medium
P. 68
More to Know! The two characteristic features seen in carbon, that is, tetravalency and catenation, put
Organic compounds
together give rise to a large number of compounds. Many have the same non-carbon
atom or group of atoms attached to different carbon chains. These compounds were
initially extracted from natural substances and it was thought that these carbon
compounds or organic compounds could only be formed within a living system. That is,
it was postulated that a ‘vital force’ was necessary for their synthesis. Friedrich Wöhler
disproved this in 1828 by preparing urea from ammonium cyanate. But carbon
compounds, except for carbides, oxides of carbon, carbonate and hydrogencarbonate
salts continue to be studied under organic chemistry.
4.2.1
4.2.1 Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon CompoundsSaturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
4.2.1 Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
4.2.1
Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
4.2.1 Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
We have already seen the structure of methane. Another compound
formed between carbon and hydrogen is ethane with a formula of C H .
2 6
In order to arrive at the structure of simple carbon
compounds, the first step is to link the carbon atoms
together with a single bond (Fig. 4.6a) and then use the
hydrogen atoms to satisfy the remaining valencies of carbon
(Fig. 4.6b). For example, the structure of ethane is arrived
in the following steps –
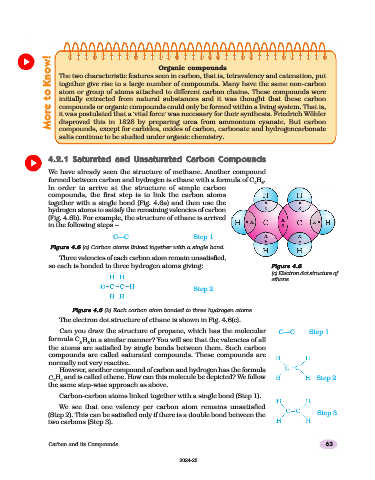
C—C Step 1
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6 (a) Carbon atoms linked together with a single bond
Three valencies of each carbon atom remain unsatisfied,
so each is bonded to three hydrogen atoms giving: Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
(c) Electron dot structure of
ethane
Step 2
Figure 4.6 (b) Each carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
Figure 4.6
The electron dot structure of ethane is shown in Fig. 4.6(c).
Can you draw the structure of propane, which has the molecular C—C Step 1
formula C H in a similar manner? You will see that the valencies of all
3 8
the atoms are satisfied by single bonds between them. Such carbon
compounds are called saturated compounds. These compounds are
normally not very reactive.
However, another compound of carbon and hydrogen has the formula
C H and is called ethene. How can this molecule be depicted? We follow Step 2
2 4
the same step-wise approach as above.
Carbon-carbon atoms linked together with a single bond (Step 1).
We see that one valency per carbon atom remains unsatisfied
(Step 2). This can be satisfied only if there is a double bond between the Step 3
two carbons (Step 3).
Carbon and its Compounds 63
2024-25