Page 100 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 100
removed completely, the object would continue
to move with the velocity it has acquired till
then.
8.2 First Law of Motion
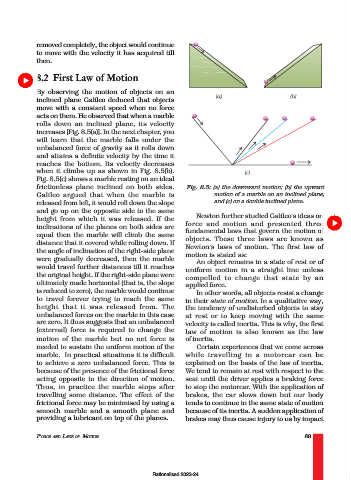
By observing the motion of objects on an
inclined plane Galileo deduced that objects
move with a constant speed when no force
acts on them. He observed that when a marble
rolls down an inclined plane, its velocity
increases [Fig. 8.5(a)]. In the next chapter, you
will learn that the marble falls under the
unbalanced force of gravity as it rolls down
and attains a definite velocity by the time it
reaches the bottom. Its velocity decreases
when it climbs up as shown in Fig. 8.5(b).
Fig. 8.5(c) shows a marble resting on an ideal
frictionless plane inclined on both sides. Fig. 8.5: (a) the downward motion; (b) the upward
Galileo argued that when the marble is motion of a marble on an inclined plane;
released from left, it would roll down the slope and (c) on a double inclined plane.
and go up on the opposite side to the same
Newton further studied Galileo’s ideas on
height from which it was released. If the
inclinations of the planes on both sides are force and motion and presented three
equal then the marble will climb the same fundamental laws that govern the motion of
objects. These three laws are known as
distance that it covered while rolling down. If Newton’s laws of motion. The first law of
the angle of inclination of the right-side plane
motion is stated as:
were gradually decreased, then the marble An object remains in a state of rest or of
would travel further distances till it reaches uniform motion in a straight line unless
the original height. If the right-side plane were
compelled to change that state by an
ultimately made horizontal (that is, the slope applied force.
is reduced to zero), the marble would continue In other words, all objects resist a change
to travel forever trying to reach the same in their state of motion. In a qualitative way,
height that it was released from. The the tendency of undisturbed objects to stay
unbalanced forces on the marble in this case at rest or to keep moving with the same
are zero. It thus suggests that an unbalanced velocity is called inertia. This is why, the first
(external) force is required to change the law of motion is also known as the law
motion of the marble but no net force is of inertia.
needed to sustain the uniform motion of the Certain experiences that we come across
marble. In practical situations it is difficult while travelling in a motorcar can be
to achieve a zero unbalanced force. This is explained on the basis of the law of inertia.
because of the presence of the frictional force We tend to remain at rest with respect to the
acting opposite to the direction of motion. seat until the driver applies a braking force
Thus, in practice the marble stops after to stop the motorcar. With the application of
travelling some distance. The effect of the brakes, the car slows down but our body
frictional force may be minimised by using a tends to continue in the same state of motion
smooth marble and a smooth plane and because of its inertia. A sudden application of
providing a lubricant on top of the planes. brakes may thus cause injury to us by impact
FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION 89
Rationalised 2023-24