Page 104 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 104
motion gives us a method to measure the force The first law of motion can be
acting on an object as a product of its mass mathematically stated from the mathematical
and acceleration. expression for the second law of motion. Eq.
The second law of motion is often seen in (8.4) is
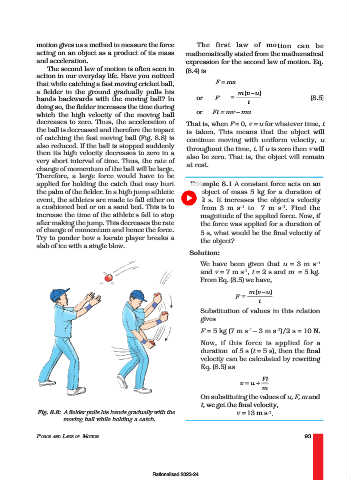
action in our everyday life. Have you noticed
that while catching a fast moving cricket ball, F = ma
a fielder in the ground gradually pulls his m ( -u )
v
hands backwards with the moving ball? In or F = (8.5)
t
doing so, the fielder increases the time during
which the high velocity of the moving ball or Ft = mv – mu
decreases to zero. Thus, the acceleration of That is, when F = 0, v = u for whatever time, t
the ball is decreased and therefore the impact is taken. This means that the object will
of catching the fast moving ball (Fig. 8.8) is continue moving with uniform velocity, u
also reduced. If the ball is stopped suddenly throughout the time, t. If u is zero then v will
then its high velocity decreases to zero in a also be zero. That is, the object will remain
very short interval of time. Thus, the rate of
at rest.
change of momentum of the ball will be large.
Therefore, a large force would have to be
applied for holding the catch that may hurt Example 8.1 A constant force acts on an
the palm of the fielder. In a high jump athletic object of mass 5 kg for a duration of
event, the athletes are made to fall either on 2 s. It increases the object’s velocity
-1
a cushioned bed or on a sand bed. This is to from 3 m s –1 to 7 m s . Find the
increase the time of the athlete’s fall to stop magnitude of the applied force. Now, if
after making the jump. This decreases the rate the force was applied for a duration of
of change of momentum and hence the force. 5 s, what would be the final velocity of
Try to ponder how a karate player breaks a the object?
slab of ice with a single blow.
Solution:
We have been given that u = 3 m s –1
-1
and v = 7 m s , t = 2 s and m = 5 kg.
From Eq. (8.5) we have,
m ( -u )
v
F =
t
Substitution of values in this relation
gives
F = 5 kg (7 m s – 3 m s )/2 s = 10 N.
-1
-1
Now, if this force is applied for a
duration of 5 s (t = 5 s), then the final
velocity can be calculated by rewriting
Eq. (8.5) as
Ft
v =u +
m
On substituting the values of u, F, m and
t, we get the final velocity,
Fig. 8.8: A fielder pulls his hands gradually with the v = 13 m s .
-1
moving ball while holding a catch.
FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION 93
Rationalised 2023-24