Page 92 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 92
Activity _____________7.10 4. What is the quantity which is
measured by the area occupied
• Feroz and his sister Sania go to school below the velocity-time graph?
on their bicycles. Both of them start at
the same time from their home but take 7.5 Equations of Motion
different times to reach the school
although they follow the same route. When an object moves along a straight line
Table 7.5 shows the distance travelled with uniform acceleration, it is possible to
by them in different times
relate its velocity, acceleration during motion
and the distance covered by it in a certain
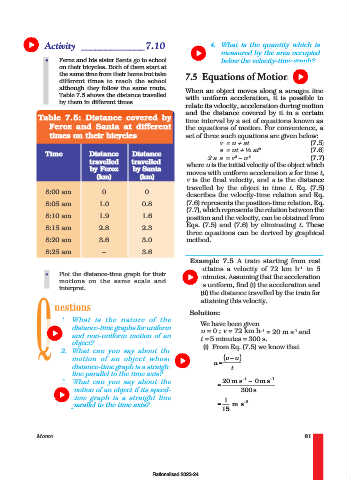
Table 7.5: Distance covered by
time interval by a set of equations known as
Feroz and Sania at different the equations of motion. For convenience, a
times on their bicycles set of three such equations are given below:
v = u + at (7.5)
s = ut + ½ at 2 (7.6)
Time Distance Distance 2 2
travelled travelled 2 a s = v – u (7.7)
by Feroz by Sania where u is the initial velocity of the object which
moves with uniform acceleration a for time t,
(km) (km)
v is the final velocity, and s is the distance
travelled by the object in time t. Eq. (7.5)
8:00 am 0 0
describes the velocity-time relation and Eq.
8:05 am 1.0 0.8 (7.6) represents the position-time relation. Eq.
(7.7), which represents the relation between the
8:10 am 1.9 1.6 position and the velocity, can be obtained from
8:15 am 2.8 2.3 Eqs. (7.5) and (7.6) by eliminating t. These
three equations can be derived by graphical
8:20 am 3.6 3.0 method.
8:25 am – 3.6
Example 7.5 A train starting from rest
attains a velocity of 72 km h –1 in 5
• Plot the distance-time graph for their minutes. Assuming that the acceleration
motions on the same scale and
interpret. is uniform, find (i) the acceleration and
(ii) the distance travelled by the train for
Q 1. What is the nature of the Solution: –1 -1
attaining this velocity.
uestions
We have been given
distance-time graphs for uniform
u = 0 ; v = 72 km h = 20 m s and
and non-uniform motion of an
t = 5 minutes = 300 s.
object?
2. What can you say about the
)
( v – u
motion of an object whose (i) From Eq. (7.5) we know that
a =
distance-time graph is a straight t
line parallel to the time axis?
3. What can you say about the 20 m s –1 – 0 m s –1
=
motion of an object if its speed- 300s
time graph is a straight line 1
parallel to the time axis? = m s –2
15
MOTION 81
Rationalised 2023-24