Page 72 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 72
Q uestions • From the above observations, answer
the following questions:
1. Which of the two onions has longer
1. What is a tissue?
roots? Why?
2. What is the utility of tissues in
2. Do the roots continue growing
multi-cellular organisms?
even after we have removed their
tips?
3. Why would the tips stop growing
6.2 Plant Tissues in jar 2 after we cut them?
The growth of plants occurs only in certain
6.2.1 MERISTEMATIC TISSUE specific regions. This is because the dividing
tissue, also known as meristematic tissue, is
located only at these points. Depending on
the region where they are present,
meristematic tissues are classified as apical,
lateral and intercalary (Fig. 6.2). New cells
produced by meristem are initially like those
of meristem itself, but as they grow and
mature, their characteristics slowly change and
they become differentiated as components of
other tissues.
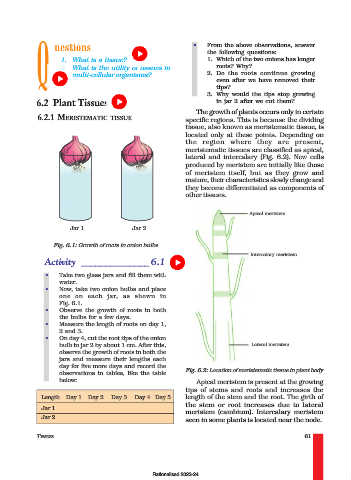
Apical meristem
Jar 1 Jar 2
Fig. 6.1: Growth of roots in onion bulbs
Intercalary meristem
Activity ______________ 6.1
• Take two glass jars and fill them with
water.
• Now, take two onion bulbs and place
one on each jar, as shown in
Fig. 6.1.
• Observe the growth of roots in both
the bulbs for a few days.
• Measure the length of roots on day 1,
2 and 3.
• On day 4, cut the root tips of the onion
bulb in jar 2 by about 1 cm. After this, Lateral meristem
observe the growth of roots in both the
jars and measure their lengths each
day for five more days and record the
observations in tables, like the table Fig. 6.2: Location of meristematic tissue in plant body
below: Apical meristem is present at the growing
tips of stems and roots and increases the
Length Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 length of the stem and the root. The girth of
the stem or root increases due to lateral
Jar 1
meristem (cambium). Intercalary meristem
Jar 2 seen in some plants is located near the node.
TISSUES 61
Rationalised 2023-24