Page 76 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 76
During breathing we inhale oxygen. Where
Q uestions does this oxygen go? It is absorbed in the lungs
1. Name types of simple tissues.
and then is transported to all the body cells
2. Where is apical meristem found?
through blood. Why would cells need oxygen?
3. Which tissue makes up the husk
The functions of mitochondria we studied
of coconut?
4. What are the constituents of
flows and carries various substances from one
phloem? earlier provide a clue to this question. Blood
part of the body to the other. For example, it
carries oxygen and food to all cells. It also
collects wastes from all parts of the body and
6.3 Animal Tissues carries them to the liver and kidney for
disposal.
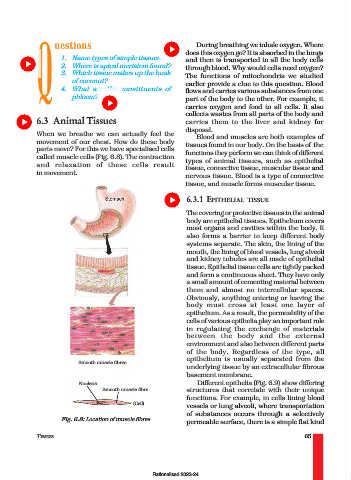
When we breathe we can actually feel the Blood and muscles are both examples of
movement of our chest. How do these body tissues found in our body. On the basis of the
parts move? For this we have specialised cells
functions they perform we can think of different
called muscle cells (Fig. 6.8). The contraction types of animal tissues, such as epithelial
and relaxation of these cells result
tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue and
in movement.
nervous tissue. Blood is a type of connective
tissue, and muscle forms muscular tissue.
6.3.1 EPITHELIAL TISSUE
The covering or protective tissues in the animal
body are epithelial tissues. Epithelium covers
most organs and cavities within the body. It
also forms a barrier to keep different body
systems separate. The skin, the lining of the
mouth, the lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli
and kidney tubules are all made of epithelial
tissue. Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed
and form a continuous sheet. They have only
a small amount of cementing material between
them and almost no intercellular spaces.
Obviously, anything entering or leaving the
body must cross at least one layer of
epithelium. As a result, the permeability of the
cells of various epithelia play an important role
in regulating the exchange of materials
between the body and the external
environment and also between different parts
of the body. Regardless of the type, all
epithelium is usually separated from the
Smooth muscle fibres
underlying tissue by an extracellular fibrous
basement membrane.
Nucleus Different epithelia (Fig. 6.9) show differing
Smooth muscle fibre structures that correlate with their unique
functions. For example, in cells lining blood
(Cell)
vessels or lung alveoli, where transportation
of substances occurs through a selectively
Fig. 6.8: Location of muscle fibres permeable surface, there is a simple flat kind
TISSUES 65
Rationalised 2023-24