Page 75 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 75
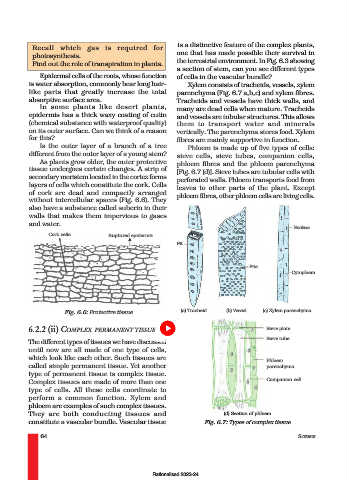
is a distinctive feature of the complex plants,
Recall which gas is required for
photosynthesis. one that has made possible their survival in
Find out the role of transpiration in plants. the terrestrial environment. In Fig. 6.3 showing
a section of stem, can you see different types
Epidermal cells of the roots, whose function of cells in the vascular bundle?
is water absorption, commonly bear long hair- Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem
like parts that greatly increase the total parenchyma (Fig. 6.7 a,b,c) and xylem fibres.
absorptive surface area. Tracheids and vessels have thick walls, and
In some plants like desert plants, many are dead cells when mature. Tracheids
epidermis has a thick waxy coating of cutin and vessels are tubular structures. This allows
(chemical substance with waterproof quality) them to transport water and minerals
on its outer surface. Can we think of a reason vertically. The parenchyma stores food. Xylem
for this? fibres are mainly supportive in function.
Is the outer layer of a branch of a tree Phloem is made up of five types of cells:
different from the outer layer of a young stem? sieve cells, sieve tubes, companion cells,
As plants grow older, the outer protective phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma
tissue undergoes certain changes. A strip of [Fig. 6.7 (d)]. Sieve tubes are tubular cells with
secondary meristem located in the cortex forms perforated walls. Phloem transports food from
layers of cells which constitute the cork. Cells leaves to other parts of the plant. Except
of cork are dead and compactly arranged phloem fibres, other phloem cells are living cells.
without intercellular spaces (Fig. 6.6). They
also have a substance called suberin in their
walls that makes them impervious to gases
and water.
Nucleus
Cork cells Ruptured epidermis
Pit
Pits
Cytoplasm
(a) Tracheid (b) Vessel (c) Xylem parenchyma
Fig. 6.6: Protective tissue
6.2.2 (ii) COMPLEX PERMANENT TISSUE Sieve plate
Sieve tube
The different types of tissues we have discussed
until now are all made of one type of cells,
which look like each other. Such tissues are
Phloem
called simple permanent tissue. Yet another parenchyma
type of permanent tissue is complex tissue.
Complex tissues are made of more than one Companion cell
type of cells. All these cells coordinate to
perform a common function. Xylem and
phloem are examples of such complex tissues.
They are both conducting tissues and (d) Section of phloem
constitute a vascular bundle. Vascular tissue Fig. 6.7: Types of complex tissue
64 SCIENCE
Rationalised 2023-24