Page 74 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 74
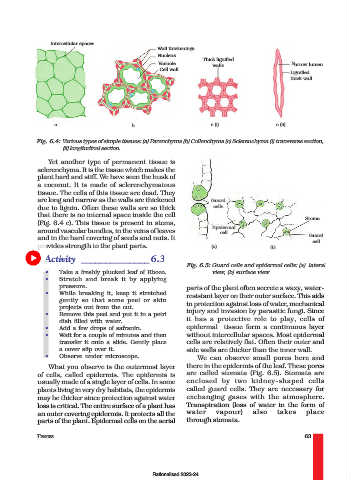
Intercellular spaces
Wall thickenings
Nucleus
Thick lignified
Vacuole walls Narrow lumen
Cell wall
Lignified
thick wall
a b c (i) c (ii)
Fig. 6.4: Various types of simple tissues: (a) Parenchyma (b) Collenchyma (c) Sclerenchyma (i) transverse section,
(ii) longitudinal section.
Yet another type of permanent tissue is
sclerenchyma. It is the tissue which makes the
plant hard and stiff. We have seen the husk of
a coconut. It is made of sclerenchymatous
tissue. The cells of this tissue are dead. They
are long and narrow as the walls are thickened Guard
due to lignin. Often these walls are so thick cells
that there is no internal space inside the cell
Stoma
(Fig. 6.4 c). This tissue is present in stems,
Epidermal
around vascular bundles, in the veins of leaves cell
and in the hard covering of seeds and nuts. It Guard
cell
provides strength to the plant parts. (a) (b)
Activity ______________ 6.3
Fig. 6.5: Guard cells and epidermal cells: (a) lateral
• Take a freshly plucked leaf of Rhoeo. view, (b) surface view
• Stretch and break it by applying
pressure. parts of the plant often secrete a waxy, water-
• While breaking it, keep it stretched resistant layer on their outer surface. This aids
gently so that some peel or skin in protection against loss of water, mechanical
projects out from the cut.
• Remove this peel and put it in a petri injury and invasion by parasitic fungi. Since
it has a protective role to play, cells of
dish filled with water.
• Add a few drops of safranin. epidermal tissue form a continuous layer
• Wait for a couple of minutes and then without intercellular spaces. Most epidermal
transfer it onto a slide. Gently place cells are relatively flat. Often their outer and
a cover slip over it. side walls are thicker than the inner wall.
• Observe under microscope. We can observe small pores here and
What you observe is the outermost layer there in the epidermis of the leaf. These pores
of cells, called epidermis. The epidermis is are called stomata (Fig. 6.5). Stomata are
usually made of a single layer of cells. In some enclosed by two kidney-shaped cells
plants living in very dry habitats, the epidermis called guard cells. They are necessary for
may be thicker since protection against water exchanging gases with the atmosphere.
loss is critical. The entire surface of a plant has Transpiration (loss of water in the form of
an outer covering epidermis. It protects all the water vapour) also takes place
parts of the plant. Epidermal cells on the aerial through stomata.
TISSUES 63
Rationalised 2023-24