Page 73 - Understanding NCERT Science 09
P. 73
Cells of meristematic tissue are very active, 3. Can we think of reasons why there
they have dense cytoplasm, thin cellulose walls would be so many types of cells?
and prominent nuclei. They lack vacuoles. Can • We can also try to cut sections of plant
we think why they would lack vacuoles? (You roots. We can even try cutting sections
of root and stem of different plants.
might want to refer to the functions of vacuoles
in the chapter on cells.)
6.2.2 (i) SIMPLE PERMANENT TISSUE
6.2.2 PERMANENT TISSUE A few layers of cells beneath the epidermis are
generally simple permanent tissue.
What happens to the cells formed by
meristematic tissue? They take up a specific Parenchyma is the most common simple
role and lose the ability to divide. As a result, permanent tissue. It consists of relatively
they form a permanent tissue. This process unspecialised cells with thin cell walls. They
of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a are living cells. They are usually loosely
arranged, thus large spaces between cells
function is called differentiation. Differentiation
leads to the development of various types of (intercellular spaces) are found in this tissue
permanent tissues. (Fig. 6.4 a). This tissue generally stores food.
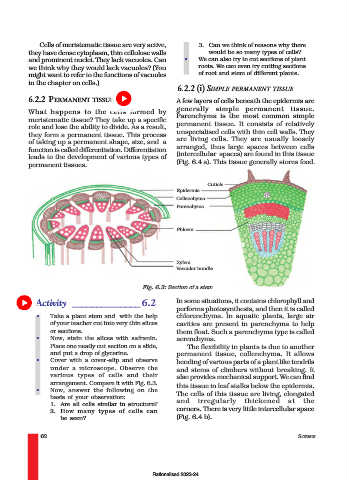
Cuticle
Epidermis
Collenchyma
Parenchyma
Phloem
Xylem
Vascular bundle
Fig. 6.3: Section of a stem
Activity ______________ 6.2 In some situations, it contains chlorophyll and
performs photosynthesis, and then it is called
• Take a plant stem and with the help chlorenchyma. In aquatic plants, large air
of your teacher cut into very thin slices cavities are present in parenchyma to help
or sections. them float. Such a parenchyma type is called
• Now, stain the slices with safranin. aerenchyma.
Place one neatly cut section on a slide, The flexibility in plants is due to another
and put a drop of glycerine. permanent tissue, collenchyma. It allows
• Cover with a cover-slip and observe bending of various parts of a plant like tendrils
under a microscope. Observe the and stems of climbers without breaking. It
various types of cells and their also provides mechanical support. We can find
arrangement. Compare it with Fig. 6.3.
this tissue in leaf stalks below the epidermis.
• Now, answer the following on the
The cells of this tissue are living, elongated
basis of your observation: and irregularly thickened at the
1. Are all cells similar in structure?
2. How many types of cells can corners. There is very little intercellular space
be seen? (Fig. 6.4 b).
62 SCIENCE
Rationalised 2023-24